Task: Iterative PET Image reconstruction
Description: The model employs a deep residual convolutional neural network to improve PET image quality by using the existing inter-patient information. An innovative feature of the proposed method is the embedding of the neural network in the iterative reconstruction framework for image representation, rather than using it as a post-processing tool. The objective function is formulated as a constrained optimization problem and solved using the alternating direction method of multipliers algorithm.
The main contributions of this paper include
- the use of dynamic data of prior patients to train a network for PET denoising and
- the integration of the neural network into the iterative reconstruction framework to demonstrate better performance than the denoising approach.
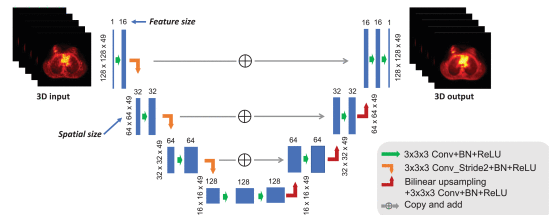
Validation: Both simulation data and hybrid real data are used to evaluate the proposed method.
The computer simulation modeled the geometry of a GE 690 scanner. Nineteen XCAT phantoms with different organ sizes and genders were employed in the simulation, seventeen for training, one for loss validation and the last one for testing. To generate the training data, 40-minutes data (20-60 min post injection) were combined into a high count sinogram and reconstructed as the label image for training. The high count data was down-sampled to 1/10th of the counts and reconstructed as the input image. In order to account for different noise levels, images reconstructed at iteration 20, 40, 60 using ML EM algorithm were all used in the training phase.
Six patient data sets of one hour FDG dynamic scan acquired on a GE 690 scanner with 5 mCi dose injection were employed in this study. Training and testing data were generated in the same way as that in the simulation. Five patient data sets were used in the training and the last one was left for testing. As no ground truth exist in the real data-sets, 5 lesions were inserted in the testing data to generate the hybrid real data-sets for quantitative analysis.
Results: Quantification results show that the proposed iterative neural network method can outperform the neural network denoising and conventional penalized maximum likelihood methods.
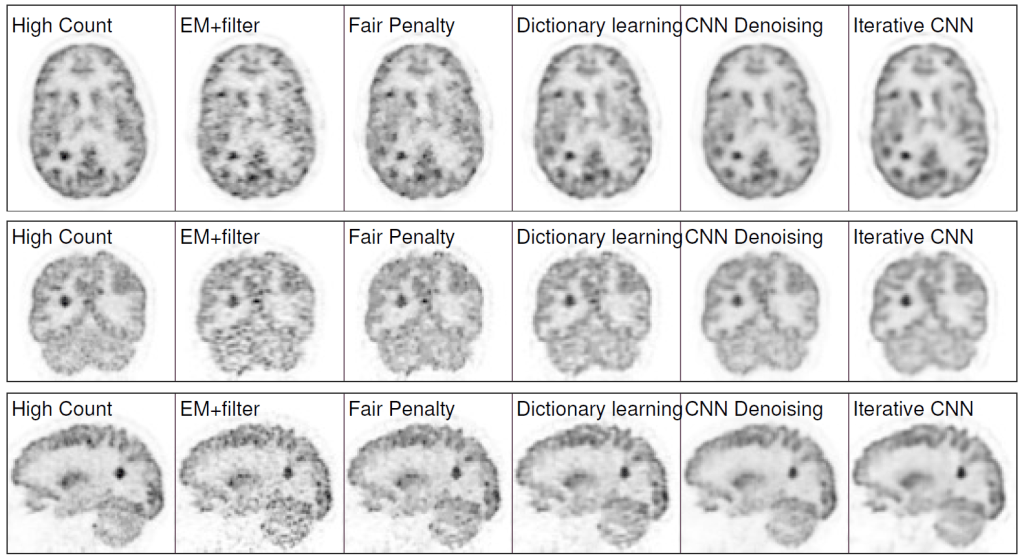
Claim: The model explores the potential of using existing inter-patient information via an iterative deep neural network to improve PET image reconstruction. The network structure is a combination of U-net structure and the residual network. Unlike existing CNN based image denoising methods, in this work a CNN was trained with iterative reconstructions of low-counts data as the input and high-counts reconstructions as the label to represent the unknown PET image to be reconstructed. Rather than feeding a noisy image into the CNN, the CNN is used to define the feasible set of valid PET images. According to the model developers, this is the first application of its kind for neural networks in medical imaging. The solution is formulated as the solution of a constrained optimization problem and sought by using the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm.
Examples: Datasets, System Matrix
