Task: Bayesian Iterative PET image reconstruction
Description: The model consists of a forward-backward splitting algorithm to integrate deep learning into maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) positron emission tomography (PET) image reconstruction. The MAP reconstruction is split into regularization, expectation-maximization (EM), and a weighted fusion. For regularization two options are offered:
- the use of either a Bowsher prior (using Markov-random fields), or
- a residual learning unit (using convolutional-neural networks) where the proposed forward-backward splitting EM (FBSEM), accelerated with ordered subsets (OS), was unrolled into a recurrent-neural network in which network parameters (including regularization strength) are shared across all states and learned during PET reconstruction.
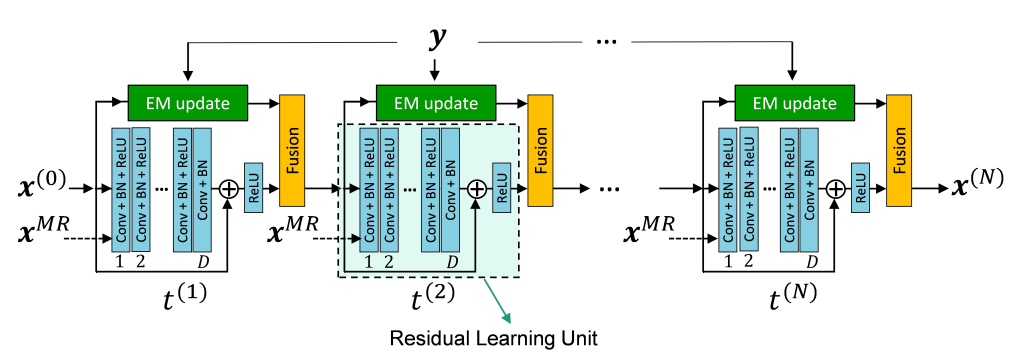
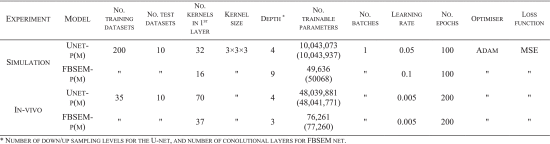
Validation: The model network was trained and evaluated using PET-only (FBSEM-p) and PET-MR (FBSEM-pm) datasets for realistic 3-D low-dose brain PET simulations and short-duration in-vivo PET-MR brain scans. It was compared to conventional ordered subsets expectation–maximization (OSEM), MR-guided Bowsher MAPEM, and a post-reconstruction U-Net denoising trained on the same PET-only (Unet-p) or PET-MR (Unet-pm) datasets.
Results: For simulations, FBSEM-p(m) and Unet-p(m) nets achieved a comparable performance, on average, 14.4% and 13.4% normalized root-mean square error (NRMSE), respectively; and both outperformed OSEM and MAPEM methods (with 20.7% and 17.7% NRMSE, respectively). For in-vivo datasets, FBSEM-p(m), Unet-p(m), MAPEM, and OSEM methods achieved average root-sum-of-squared errors of 3.9%, 5.7%, 5.9%, and 7.8% in different brain regions, respectively. In conclusion, the studied U-Net denoising method achieved a comparable performance to a representative implementation of the FBSEM net.

Remarks: The basic novel features introduced by the model are:
- an optimization algorithm for Bayesian maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) PET image reconstruction, which generalizes De Pierro’s MAPEM algorithm for any differentiable convex prior;
- unrolling of the resulting algorithm into a model-based deep reconstruction network in which CNNs are used to learn image features while activity images are reconstructed from emission data;
- learning of any hyperparameter from data;
- optional incorporation of anatomical side information into PET reconstruction without substantial suppression of PET unique features as seen with conventional MR-guided reconstruction algorithms; and
- investigation of whether deep reconstruction methods can outperform DL-based denoising methods and whether the redesign of the current reconstruction workflow for PET scanners is justified, which would be required for clinical deployment.
Claim: A model-based DL reconstruction network was designed by unrolling a novel a proximal splitting optimization algorithm for Bayesian MAPEM image reconstruction. The proposed FBSEM net was evaluated in PET-only and PET-MR modes in comparison with the state-of-the-art U-Net denoising and conventional MR-guided MAPEM and standard OSEM methods. Simulation and in-vivo results showed that both DL-based techniques outperform the conventional methods, while the Unet-p and FBSEM-p net achieve a fairly comparable performance for both simulation and in-vivo datasets. DL-based post-reconstruction denoising methods can potentially perform as good as DL-based reconstruction methods.
