Task: Low-dose PET image denoising via a GAN method
Description: A hybrid 2D and 3D parameter-transferred Wasserstein GAN PT-WGAN model for low-dose PET image denoising. The model’s performance is a tradeoff between computational effectiveness and denoising performance.
The generator of PT-WGAN is designed for noise reduction, and consists of 2D and 3D encoder-decoder structures. There are typical convolution operators and deconvolution operators in the encoder and decoder, respectively. In the generator, 3-D convolution operators are applied followed by 2-D convolution operators to combine features in the 3D and 2D domains, bridging the gap between the 3D and 2D feature spaces and saving computational resources. Convolution operators are used to capture the abstraction of image contents while reducing noise and corruption. Deconvolution operators are then used to recover image details.
The mean squared error (MSE) is first used as the loss function to train the generator of the proposed network separately. In the next training phase, the task-specific initialization is leveraged instead of using the Xavier initialization. Specifically, the generator is initialized from the parameters of the pretrained model. Thus, the two basic novel features of the model are :
- a PT-WGAN framework designed to denoise low-dose PET images without compromising structural details, and
- a task-specific initialization based on transfer learning developed to train PT-WGAN using trainable parameters transferred from a pretrained model, which significantly improves the training efficiency of PT-WGAN.

Results: The experimental results on clinical data show that the proposed network can suppress image noise more effectively while preserving better image fidelity than three other recently published state-of-the-art models: RED-CNN , DCNN , and CPCE-3D-GAN.

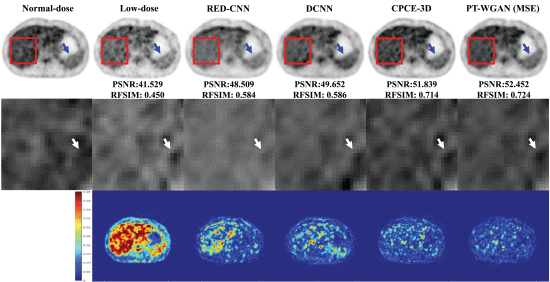
Claim: Compared with the RED-CNN and DCNN, the CPCE-3D obtained better quantitative metrics, especially regarding RFSIM and VIF. In reference to the error map, the CPCE-3D approach suppressed more noise than did the RED-CNN and DCNN approaches. The denoising effect of the PT-WGAN (MSE) exhibits a certain improvement compared with that of the CPCE-3D. In terms of the four quantitative metrics, namely, PSNR, NRMSE, RFSIM, and VIF, the PT-WGAN network achieved the best results. Further work is in progress to improve the performance of low-dose PET denoising according to the model’s developers.
