Task: Whole body attenuation map generation using 3D U-Net generative adversarial networks (GANs)
Description: The model is initially trained as a 3D U-Net to learn the mapping from non attenuation corrected 18-F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET images to a synthetic Computerized Tomography (sCT) and also to label the input voxel tissue. The sCT image is further refined using an adversarial training scheme to recover higher frequency details and lost structures using context information (3D GAN).
Validation: The model is trained and tested on public available datasets, containing several PET images from different scanners with different radiotracer administration and reconstruction modalities. The network is trained with 108 samples and validated on 10 samples.
Results: The mean absolute error in the sCT images is 90±20 and 103±18HU with a peak signal to noise ratio of 19.3±1.7 dB and 18.6±1.5, for the base model and the adversarial model respectively. The attenuation correction is tested by means of attenuation sinograms, obtaining a line of response attenuation mean error lower than 1% with a standard deviation lower than 8%. The generated images show good correlation with the unknown structural information.
Remarks: The GAN-synthesized image quality is comparable to the base U-Net method with small attenuation sinograms differences, thus demonstrating its potential for quantitative PET image correction.
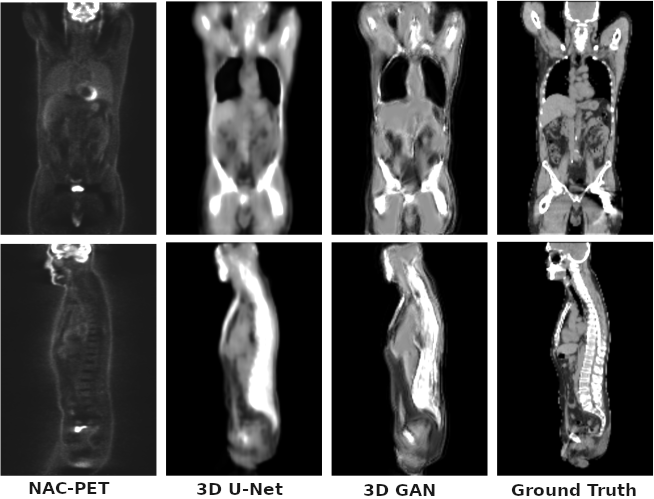
The bone tissue is presented using a 3D projection in the following image:

Claim: The proposed deep learning topology, as trained, validated and tested on publicly available data sets form multiple sources and modalities, is capable of generating whole body attenuation maps of high accuracy from uncorrected 18F-FDG PET image data.
Datasets (for training and validation)
